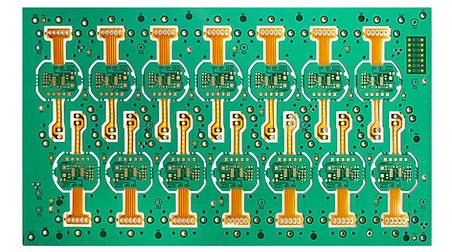
What is a Rigid-flex PCB?
A rigid-flex PCB combines rigid and flexible PCB technologies into a single hybrid design. This type of printed circuit board features both rigid sections for mounting components and flexible sections for bending or folding, offering durability and versatility.
This hybrid design:
Reduces connectors and cables
Simplifies assembly and improves reliability
Supports miniaturization and complex 3D geometries·
Explore our Ultimate Guide to Rigid-Flex PCB Design & Manufacturing to dive deeper.
Stack-up and Materials
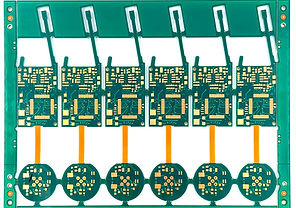
Rigid-flex PCB combines the advantages of rigid PCB and flex PCB. It is made of flexible material layered on top of rigid material, creating a board that is rigid in some parts and flexible in others. From the picture beside, you can clearly understand the stacking structure of Rigid-flex circuit board.
Understanding materials is key to rigid-flex performance:
Conductors:
Copper types: RA, HA, ED
Common thicknesses: 1/3 oz, 1/2 oz, 1 oz, 2 oz
Adhesives: Selected based on conductor type and end-use
Dielectrics: PI film, FR-4, solder mask
Thickness: 25 ~ 125 um
Surface Finishes: ENIG, ENEPIG, hard gold, tin, OSP, silver
For more details about flexible PCB manufacturing, visit our Flexible PCB Guide.

Stack-up of Rigid-flex PCB
Benefits
-
Manufacturing Process:
-
Rigid-flex PCB combines the benefits of rigid and flexible circuit boards, enabling complex 3D designs.
-
Reduces the need for connectors and cables, simplifying assembly.
-
-
Logistics and Transportation:
-
Lower weight and compact design reduce shipping costs.
-
Enhanced durability during transportation due to fewer mechanical parts.
-
-
Electronic Assembly:
-
Streamlined assembly with integrated rigid and flexible sections.
-
Higher reliability due to fewer solder joints and interconnections.
-
Facilitates miniaturization of devices while maintaining functionality.
-
Applications
-
Aerospace and military: Used in environments requiring high reliability, such as satellites and flight control systems.
-
Consumer products: Used in high-end smartphones, tablets, wearable tech, robot vacuum cleaners, etc.
-
Automotive: Used in in-vehicle entertainment systems, sensors, and power systems.
-
Medical devices: Rigid-flex PCB suitable for modern medical equipment, such as vital sign monitoring instruments and embedded medical sensors.
Advanced Features
-
Highly customized: Rigid-flex circuit board supports complex shape design and multiple application requirements.
-
High-reliability connection: Rigid-flex PCB combination reduces electrical connection points and improves the overall reliability of the system.
-
Versatility: Suitable for complex systems that require multiple mechanical and electrical properties.
Essential Aspects of Rigid-Flex PCB Design and Production
Conductors:
Copper is the most commonly used material for constructing flex PCB and rigid-flex PCB. It is available in various thicknesses to meet the specific requirements for current capacity and voltage drop, usually specified in ounces per square foot. Typical thicknesses include 1/3 oz (12um), ½ oz (15um), 1 oz (35um), and 2 oz (70um). Copper options have RA, ED copper and HA copper.

Adhesives:
The choice of adhesive depends on customer specifications and conductor thickness.
Insulators/Dielectrics:
Flexible substrates and coverlay materials come in various thicknesses, ranging from 25um to 125um. Common dielectric materials include PI film, FR-4, and solder mask.
Surface Finishes:
The final surface finish of flex PCB depends on the assembly requirements and application of the product. Common finishes include ENIG, ENEPIG, hard nickel/gold, tin, OSP, and silver.
Air Gap:
Selective bonding techniques are used to increase flexibility by “unbonding” layers, allowing them to flex freely. As a professional rigid-flex PCB manufacturer, Flex Plus supports air gap technology applications, providing additional flexibility in designs.
Controlled Impedance:
As signal switching speeds increase, it becomes critical for engineers to manage the impedance of sensitive signal lines. For modern digital circuits, which have fast signal transitions and high clock rates, traces should be treated as transmission lines to prevent electrical reflections and ensure smooth signal transitions. Designing controlled impedance traces requires precise control over the physical dimensions of the etched copper traces and the thickness of the dielectric materials to maintain uniformity in electrical properties.
Panelization:
Multiple circuits are partially routed with breakaway tabs, enabling them to remain in a panel for component assembly during the pick-and-place and wave soldering processes. As a rigid-flex PCB manufacturer, we ensure that after assembly, the rigid-flex circuits can be easily separated by V-cut or stamp holes, making them ready for final product integration.

PSA (Pressure Sensitive Adhesive):
PSA is commonly used to bond mechanical stiffeners to flex circuit board and rigid-flex PCB. They also serve in applications where part of the circuit needs to be secured in place within the final product. The release liner is peeled off during assembly, exposing the adhesive, which allows the circuit to be pressed into position and remain securely in place.
Shielding:
Shielding is essential when controlled impedance and/or limits on electromagnetic or electrostatic interference are required. Common shielding materials include copper, shielding film, and silver or carbon ink.
To design with reliability in mind, see our Rigid Flex PCB Design Best Practices.
Component Assembly & Testing
We offer:
-
Through-hole & SMT assembly, COB assembly.
-
In-circuit testing
-
Conformal coating
-
ESD protective packaging
Want to understand the cost factors? Read Why Flexible PCBs Cost More Than Rigid PCBs.

Rigid vs Flex vs Semi-Flex
Choosing the right printed circuit board type depends on:
-
Mechanical requirements
-
Cost considerations
-
Assembly complexity
FAQ
Q: What’s the benefit of combining rigid and flexible boards?
A: It improves reliability, saves space, and reduces assembly steps.
Q: What materials are used in rigid-flex PCB?
A: Copper, PI film, adhesives, and various surface finishes like ENIG.
Q: Can rigid-flex PCB be used in medical devices?
A: Yes, especially in compact and reliable embedded systems.
Looking for a trusted rigid-flex PCB manufacturer? Contact us today for engineering support or a quick quote!

